introduction
Guava, a fruit synonymous with tropical paradise and vibrant flavour, is a true gem of nature’s gift. Originating from the tropical regions of Central America, the guava plant, scientifically known as Psidium guajava, has made its mark across the world, captivating the taste buds with its unique combination of sweetness and tartness. Revered for its rich nutritional profile and versatility, guava holds a special place in culinary traditions, medicinal practices and cultural celebrations across the world.
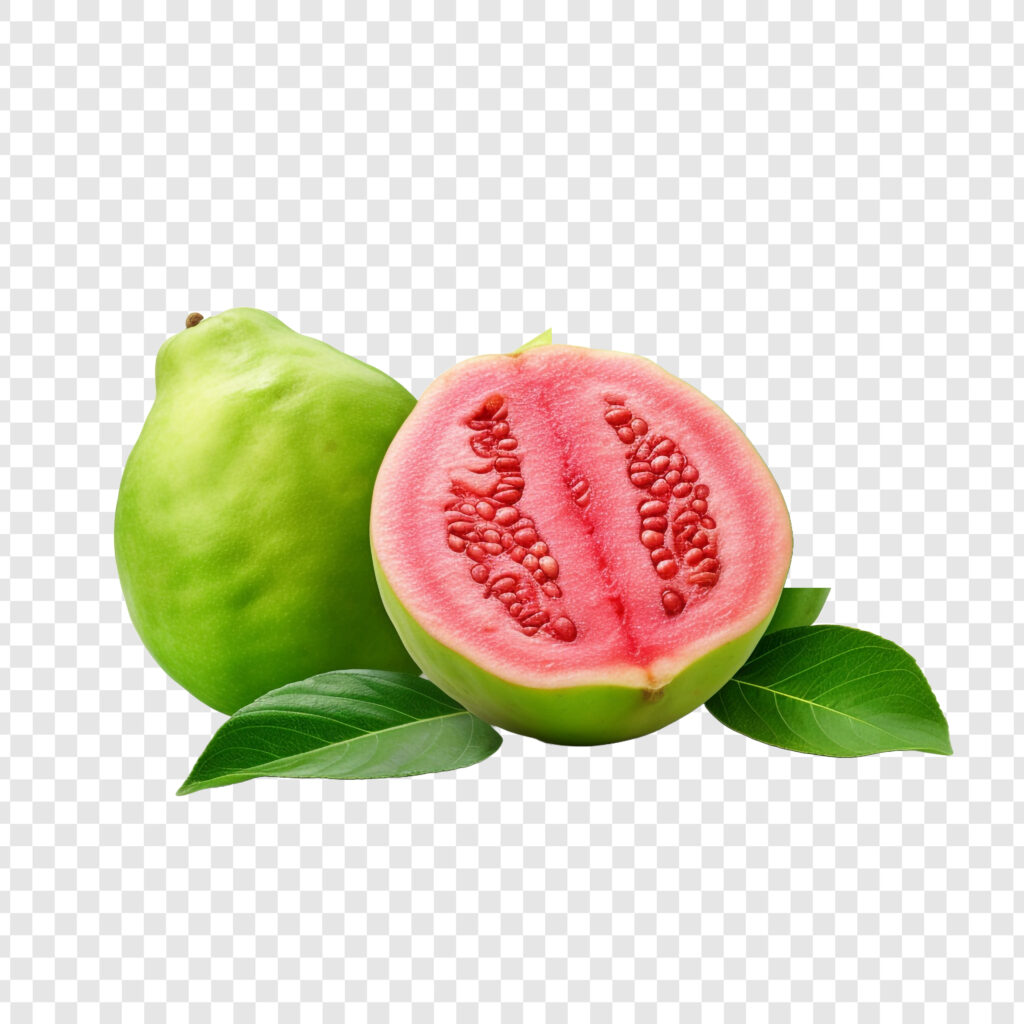

As one of the most widely cultivated fruits in tropical and subtropical regions, guava thrives in diverse climates, from humid rainforests to arid landscapes, thriving in both backyard gardens and commercial orchards alike. Is. Its distinctive round or oval shape, varying in size and color depending on the variety, hides a juicy pulp that ranges from creamy white to vibrant pink or orange, filled with juicy pulp and edible seeds.
In addition to its unique flavor, guava boasts an impressive array of health benefits, earning its reputation as a nutritional powerhouse. Rich in essential vitamins, minerals and antioxidants including Vitamin C, Vitamin A, potassium and fiber, it provides a natural boost to the immune system, promotes digestive health and supports overall well-being.
Origin of guava
Guava is believed to have originated in an area stretching from southern Mexico to Central America. It has been cultivated and consumed by indigenous people for centuries, its exact origins dating back thousands of years. Archaeological evidence shows that guava was domesticated by ancient civilizations such as the Maya and Aztecs.
From its native habitat in Central America, guava spread to other tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Caribbean, South America, Asia, Africa, and the Pacific Islands. Its adaptability to different climate and soil conditions facilitated its widespread cultivation and integration into local culinary traditions.
Spanish and Portuguese explorers played an important role in the global spread of guava during the colonial era. They introduced guava to areas such as the Philippines, India, and Southeast Asia, where it became established as a popular fruit crop.
Today, guava is cultivated commercially in many countries with tropical and subtropical climates, including Brazil, India, Thailand, Mexico, Colombia, and Indonesia. Its popularity is increasing across the world due to its delicious taste, nutritional value and versatility in culinary applications.
types of guava
Guava, a versatile and delicious fruit, comes in different types and varieties, each of which has its own unique characteristics in terms of taste, aroma, texture and appearance.



Common guava : it is, also known as apple guava, is widely cultivated in the United States, especially in Florida, California, Hawaii, and Texas. It is known for its greenish-yellow skin and white to pinkish flesh. Common guava is often used to make juices, jams and sweets.
Pink Supreme Guava: This variety of guava is famous for its large size and pink pulp, which is sweeter and more aromatic than the common guava. Pink Supreme guavas are commonly grown in Florida and California.
Red Malaysian Guava: Red Malaysian guava has red skin and pink flesh with a sweet and tart flavor. It is popular for eating fresh and making preserves. This variety is cultivated in areas like Florida and California.
Ruby x Guava: Ruby x Guava is a hybrid variety with red peel and pink pulp. It is prized for its extraordinary sweetness and juiciness. This type of guava is grown in warmer regions of the US, including Florida and California.
White Indian Guava: White Indian guava has greenish-yellow skin and white pulp with a sweet and mild flavor. It is commonly grown in Florida, especially in the Indian River region, and is loved for its smooth texture and delicate flavor.
Mexican Cream Guava: Mexican cream guava is distinguished by its creamy white pulp and sweet, aromatic flavor. It is popular for fresh eating and making sweets. This variety is cultivated in warm climate areas like Florida and California.
These are some examples of the types of guava grown in the United States. Other varieties and varieties can also be found in different states across the country, depending on specific growing conditions and growers’ preferences.
Here are few more types of guava in the world
Strawberry guava : Also known as Catley guava or cherry guava, it produces small, round fruits with red skin and pink flesh, which have a distinct strawberry-like flavor.
Pineapple guava : Although not a true guava, it is sometimes called guava or guava pineapple. It has green skin and sweet, aromatic pulp that tastes like pineapple, banana and mint.
Lemon Guava: Yellow-green skin and tart pulp with lemon flavor.
Crystal Guava: A type of guava with translucent pulp and a sweet, mild flavor.
Seedless Guava: A variety with few or no seeds, making it easy to eat fresh or use in culinary applications.
Honey Yellow Guava: A variety with golden-yellow skin and a sweet, honey-like flavor.
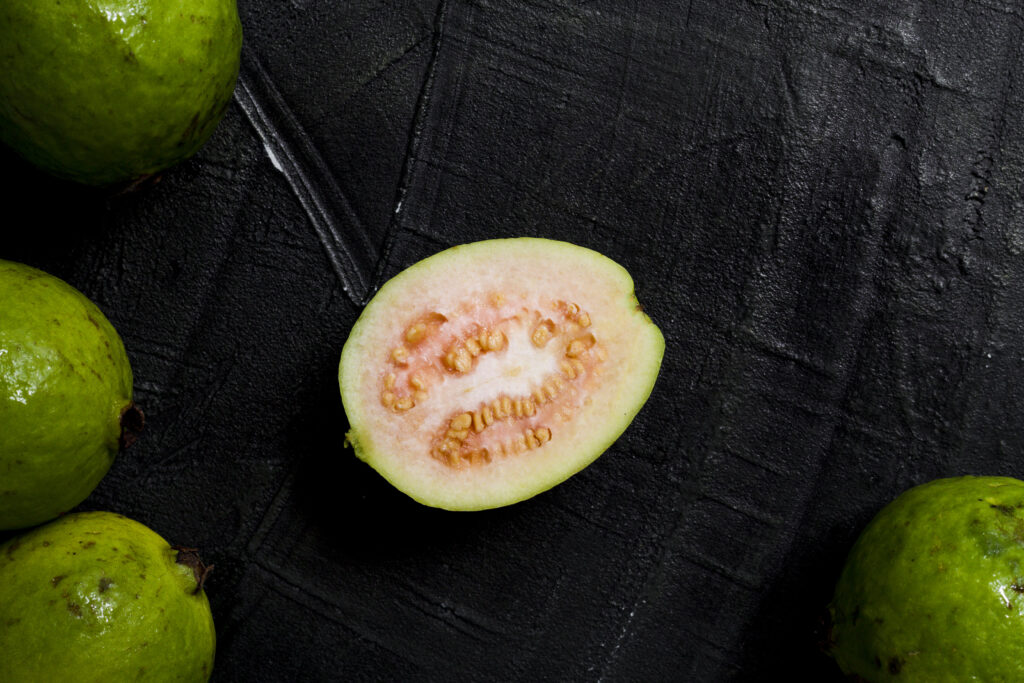
internal color of guava is pink or white....why?
Pink Guava: Pink-fleshed guavas typically contain high levels of carotenoids, especially lycopene. Lycopene is a natural pigment that gives fruits and vegetables their red or pink color. In pink guava, the presence of lycopene contributes to the pink color of the pulp. Pink guavas are often sweeter and have a more pronounced flavor than white-fleshed guavas.
White Guava: On the other hand, white-fleshed guavas have a lower concentration of pigments like lycopene. Instead, white guava pulp may contain high levels of vitamin C and other compounds such as flavonoids. The absence of pigments results in the color of the flesh being white or pale yellow. White guava has a milder taste than pink guava.
It is important to note that the internal color of guava can also be affected by factors such as maturity, growing conditions, and environmental factors. For example, as guavas ripen, they may develop darker colors, including pink or yellow. Additionally, soil quality, climate, and exposure to sunlight can affect the nutritional content and pigmentation of the fruit.
nutrition in guava
Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
Calories | 68 |
Protein | 2.6 grams |
Carbohydrates | 14.3 grams |
Dietary Fiber | 5.4 grams |
Sugars | 9 grams |
Fat | 0.9 grams |
Vitamin C | 228.3 mg (254% DV) |
Vitamin A | 624 IU (13% DV) |
Potassium | 417 mg (9% DV) |
Calcium | 18 mg (1.5% DV) |
Iron | 0.26 mg (1.5% DV) |
Magnesium | 22 mg (5% DV) |
Phosphorus | 40 mg (6% DV) |
Vitamin B6 | 0.11 mg (7% DV) |
Folate | 49 µg (12% DV) |
Please note that the nutritional composition may vary slightly depending on factors such as variety, ripeness, and growing conditions.
may helps in hair

Guava offers many nutritional benefits that may contribute to the growth and maintenance of healthy hair.
Vitamin C: Guava is rich in Vitamin C, it has more of this nutrient than orange. Vitamin C is essential for the production of collagen, a protein that helps strengthen hair, prevent breakage, and promote hair growth. It also acts as an antioxidant, protecting hair follicles from damage caused by free radicals.
Biotin (Vitamin B7): Biotin is another important nutrient for hair health, and guavas contain significant amounts of it. Biotin helps metabolize amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. Since hair is primarily made up of protein, biotin plays an important role in maintaining the strength and structure of hair.
Vitamin A: Guava is a good source of vitamin A, which is essential for the production of sebum, the natural oil that moisturizes the scalp and keeps hair hydrated and healthy. Adequate vitamin A intake also aids in the growth of strong, shiny hair.
Iron: Iron deficiency is linked to hair loss, so eating iron-rich foods like guava can help prevent hair thinning and promote healthy hair growth. Iron is essential for delivering oxygen to the hair follicles, stimulating growth, and maintaining hair health.
Antioxidants: Guava contains various antioxidants, including vitamin C and flavonoids, which help protect hair follicles from damage caused by oxidative stress and environmental factors. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants support overall scalp health and promote optimal conditions for hair growth.
.
may helps in heart
Guava offers many nutritional benefits that may contribute to the growth and maintenance of healthy hair.
Dietary Fiber: Guava is an excellent source of both soluble and insoluble dietary fiber. Soluble fiber helps reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive tract and removing it from the body. Insoluble fiber promotes regular bowel movements and helps prevent constipation, which may indirectly benefit heart health by reducing the risk of digestive disorders.
Vitamin C: Guava is one of the richest sources of Vitamin C among fruits. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the heart from oxidative stress and inflammation, which are risk factors for heart disease. Additionally, vitamin C supports the health of blood vessels by promoting the synthesis of collagen, a protein that provides structural support to arteries and veins.
Potassium: Guava is a good source of potassium, a mineral that plays an important role in controlling blood pressure. Potassium helps counteract the effects of sodium, lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of high blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
Low Glycemic Index: Guava has a relatively low glycemic index (GI), which means it causes a gradual and steady rise in blood sugar levels compared to higher-GI foods. Consuming low GI foods like guava can help control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome, all risk factors for heart disease.
Including guavas along with other nutrient-rich foods like vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins in a heart-healthy diet may contribute to overall heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease. However, to achieve optimal heart health, it is essential to maintain a balanced diet and lifestyle, including regular physical activity and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.

may helps in skin

Skin brightening: The high Vitamin C present in guava can help in skin brightening and reducing dark spots, hyperpigmentation and uneven skin tone. Vitamin C inhibits melanin production, which is the pigment responsible for dark spots, making the complexion more radiant.
Hydration: Guava is rich in water, which helps in keeping the skin hydrated and moist. Proper hydration is essential for maintaining skin health, as it helps prevent dryness, flakiness, and irritation.
Wound healing: Vitamin C and other antioxidants in guava may promote wound healing and repair damaged skin. Vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis, which is important for the formation of new skin tissue and the healing of wounds, cuts and scars.
Acne prevention: Guava has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties that may help prevent acne breakouts and reduce inflammation associated with acne-prone skin. Additionally, the vitamin C content in guava may help control sebum production, reduce excess oiliness, and prevent clogged pores.
Detoxification: Guava is rich in dietary fiber and antioxidants, which help support the body’s natural detoxification processes. By eliminating toxins and impurities from the body, guava can help promote clear, healthy-looking skin.
Adding guava to your diet or using guava-based skin care products can help improve skin health and brighten your complexion. However, it is essential to maintain a balanced diet, stay hydrated and follow a proper skin care routine to get the best results for your skin.
may helps in eye
Vitamin A: Guava is a good source of vitamin A, which is essential for maintaining healthy vision. Vitamin A plays an important role in the function of the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, and helps prevent night blindness and dry eyes. Adequate vitamin A intake is also linked to a reduced risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of vision loss in older adults.
Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Guava contains lutein and zeaxanthin, two carotenoids that are concentrated in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. Lutein and zeaxanthin act as natural sunscreens, filtering out harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays and blue light, which can damage the eyes and contribute to AMD and cataracts.
Including guava in your diet as part of a balanced and nutritious meal plan can help with overall eye health and reduce the risk of eye-related conditions. However, it is essential to combine guava consumption with other eye-healthy habits, such as wearing sunglasses outside, practicing good hygiene and getting regular eye exams to maintain optimal vision and eye health.

summary
Guava, scientifically known as Psidium guajava, is a tropical fruit native to Central and South America, but is now cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions around the world. This fruit is famous for its unique taste, which is a mixture of sweet and slightly tart tastes and its distinctive aroma. Guavas are usually round or oval shaped with green or yellow peel depending on the variety, and the pulp can range from white to pink, containing many small seeds. Apart from its delicious taste, guava is highly regarded for its nutritional value. It is rich in vitamin C, fiber, antioxidants and various essential nutrients, making it a healthy addition to any diet. Guava is also associated with several health benefits, including better digestion, a stronger immune system, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and some types of cancer.
Apart from fresh consumption, guava is also used to make juices, jams, jellies and sweets. The leaves of the guava tree are also used in traditional medicine for their medicinal properties, including the ability to lower blood sugar levels and ease diarrhea.
Overall, guava is a versatile and nutritious fruit that not only delights the taste buds but also contributes to overall health and well-being.
frequently asked questions
What are the nutritional benefits of guava?
Guava is rich in vitamin C, providing over 200% of the daily recommended intake. It’s also a good source of dietary fiber, aiding digestion and promoting gut health. Additionally, it contains vitamin A, potassium, and antioxidants, contributing to overall immunity, skin health, and cardiovascular well-being.
How is guava utilized in the cosmetic and skincare industry?
Guava is used in skin care products due to its high vitamin C content, which brightens the skin and promotes collagen production, reducing wrinkles and fine lines. Its antioxidants help protect against environmental damage, while its astringent properties help tone and tighten the skin, making it a popular ingredient in creams, serums and masks.
How does guava cultivation differ in different climates and regions?
Guava cultivation varies based on climate and region. In tropical areas, it thrives in warm, humid conditions, while in subtropical regions, it can tolerate cooler temperatures. Cultivation practices may differ in terms of irrigation, pest management, and pruning techniques, tailored to the specific environmental conditions of each area.
what are the benefits of guava leaves?
Guava leaves provide many health benefits. They have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, which aid wound healing and prevent infection. Additionally, they are rich in antioxidants such as flavonoids and tannins, which when consumed as tea or extract may help lower blood sugar levels, lower LDL cholesterol, and promote overall heart health.
What are some common pests and diseases that affect guava plants?
Common pests affecting guava include fruit flies, aphids, and mealybugs, which damage fruits and leaves. Diseases like anthracnose, caused by fungi, lead to fruit rot, while bacterial diseases like guava wilt can cause wilting and death. Proper sanitation, pruning, and use of pesticides are key for management.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication .health-live.store does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.